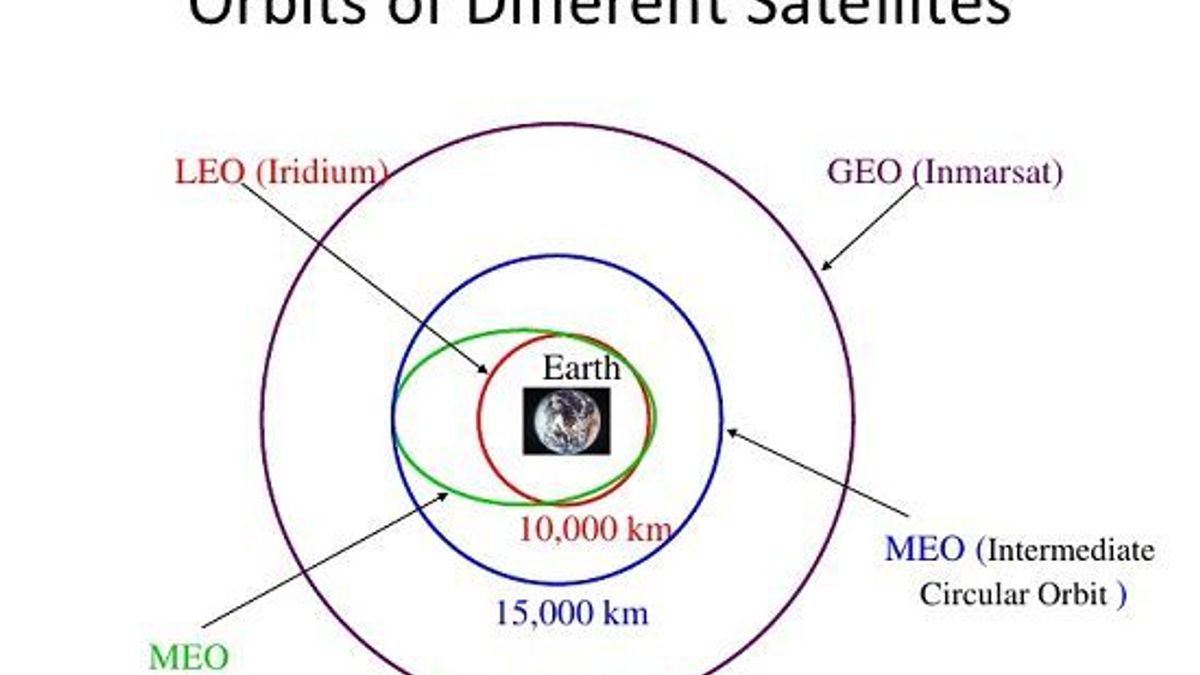
- Earth Orbit Diagram
- How High Is Low Earth Orbit
- Earth Orbit Animation
- How Many Satellites Orbit Earth
- Earth Orbits The Sun
Milankovitch cycles include the shape of Earth’s orbit (its eccentricity), the angle that Earth’s axis is tilted with respect to Earth’s orbital plane (its obliquity), and the direction that Earth’s spin axis is pointed (its precession). These cycles affect the amount of sunlight and therefore, energy, that Earth absorbs from the Sun. Earth orbits the sun once a year and rotates on its axis once a day. The Earth’s orbit makes a circle around the sun. At the same time the Earth orbits around the sun, it also spins. In science, we call that rotating on its axis. Pluto 's orbit is exceptional in that its orbit makes an angle of 17° with the Earth's orbit. This has led to a number of theories about Pluto's origin. Mercury is the only other planet which moves significantly away from the ecliptic plane ( 7°). Index Gravity concepts Orbit concepts.
Earth Orbit Diagram

Englsh-Russian aviation and space dictionary. - M.: Military publishing house USSR Ministry of Defence. edited by M. Murashkevich. 1974.
Смотреть что такое 'orbit the earth' в других словарях:
The Day the Earth Caught Fire — Infobox Film name = The Day the Earth Caught Fire |175px caption = film poster director = Val Guest producer = Val Guest Frank Sherwin Green writer = Wolf Mankowitz Val Guest starring = Janet Munro Leo McKern Edward Judd music = Stanley Black… … Wikipedia
The Earth Sings Mi Fa Mi — Infobox Album Name = The Earth Sings Mi Fa Mi Type = studio Artist = The Receiving End Of Sirens Released = August 7, 2007 Recorded = SOMD Studios, Beltsville, MD. The Llama Farms, CT. Mixed = SOMD Studios, Beltsville, MD. Genre = Experimental… … Wikipedia
Structure of the Earth — Earth cutaway from core to exosphere. Left picture is not to scale. The interior structure of the Earth, similar to the outer, is layered. These layers can be defined by either their chemical or their rheological properties. The Earth has an… … Wikipedia
History of the Earth — For the history of modern humans, see History of the world. Geological time put in a diagram called a geological clock, showing the relative lengths of the eons of the Earth s history The history of the Earth describes the most important events… … Wikipedia
Properties of the Moon and the Earth-Moon system — ▪ Table Properties of the Moon and the Earth Moon system Moon Earth approximate ratio (Moon to Earth) mean distance from Earth (orbital radius) 384,400 km period of orbit around Earth (sidereal period of revolution) 27.3217 Earth days inclination … Universalium
Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System — Artist representation of CERES instruments scanning Earth in Rotating Azimuth Plane mode. Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) is on going[update] NASA climatological experiment from Earth … Wikipedia
From the Earth to the Moon — This article is about the Jules Verne novel. For the 1958 film adaptation, see From the Earth to the Moon (film). For the unrelated miniseries, see From the Earth to the Moon (TV miniseries). From the Earth to the Moon … Wikipedia
Apex of the earth's motion — Apex A pex, n.; pl. E. {Apexes}; L. {Apices}. [L.] 1. The tip, top, point, or angular summit of anything; as, the apex of a mountain, spire, or cone; the apex, or tip, of a leaf. [1913 Webster] 2. (Mining) The end or edge of a vein nearest the… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
The NoZe Brotherhood — The Noble NoZe Brotherhood, Congress Photo for The Rope, Spring 2006 The NoZe Brotherhood is a collegiate secret society at Baylor University. Founded in Brooks Hall in 1924, the society was originally formed as a joke regarding Leonard Shoaf, a… … Wikipedia
Orbit of the Moon — Not to be confused with Lunar orbit in the sense of a selenocentric orbit, that is, an orbit around the Moon The Moon completes its orbit around the Earth in approximately 27.3 days (a sidereal month). The Earth and Moon orbit about their… … Wikipedia
Earth — This article is about the planet. For other uses, see Earth (disambiguation). Earth … Wikipedia
How High Is Low Earth Orbit
Книги
- The Theory of Scintillation with Applications in Remote Sensing, Charles Rino. In order to truly understand data signals transmitted by satellite, one must understand scintillation theory in addition to well established theories of EM wave propagation and scattering.… ПодробнееКупить за 9521.78 рубэлектронная книга
- The History of Space Exploration. Discoveries from the Ancient World to the Extraterrestrial Future, Roger D. Launius. For centuries humanity has engaged in a virtual exploration of space through astronomical observation, aided by astounding scientific and technological advances. In more than sixty years… ПодробнееКупить за 3564 грн (только Украина)
- The Complete Earth: A Satellite Portrait of Our Planet, Douglas Palmer. Data from NASA's most advanced Earth satellites has been combined to create the most detailed global portrait of our planet ever created - here this photomap is reproduced in its astonishing… ПодробнееКупить за 3210 руб
To celebrate Earth Day, we are sharing stunning views of our beautiful planet, captured by NOAA satellites.

Since 1970, NOAA satellites have been monitoring Earth’s weather, environment, oceans, and climate. They provide critical information that feeds forecasts and warns us of severe weather and environmental hazards. NOAA operates two primary types of satellites: geostationary and polar-orbiting.
Geostationary satellites orbit 22,236 miles above the equator at speeds equal to Earth’s rotation. This means they continuously view the same area. Because they stay above a fixed spot on the surface, they provide constant vigil to identify and track severe weather conditions and environmental hazards. Information from geostationary satellites is used for short-term (1-2 day) forecasts and also for tracking storm systems in real-time.
Earth Orbit Animation
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites – R Series (GOES-R) is NOAA’s newest generation of geostationary satellites. GOES-16, in operations as GOES East, keeps watch over most of North America, including the contiguous United States and Mexico, as well as Central and South America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west coast of Africa. GOES-17, which serves as GOES-West, watches over the western continental United States, Alaska, Hawaii, and the Pacific Ocean to New Zealand.
GOES-16 and GOES-17 each carry an imager and a lightning mapper that provide critical data about Earth’s weather and environment.
Polar-orbiting satellites circle the globe from the North Pole to the South Pole 14 times a day. They image the entire Earth at least twice daily, from 512 miles above its surface. Earth rotates counterclockwise underneath the path of the satellites, resulting in a different view with each orbit.
Global data from polar-orbiting satellites, including atmospheric temperature and moisture profiles, are used in numerical weather models to generate weather forecasts up to seven days out. Polar-orbiting satellites observe the whole world in higher resolution than GOES satellites, allowing for a broader and more detailed view of weather patterns and environmental conditions.
NOAA’s polar-orbiting satellites, the Joint Polar Satellite System’s (JPSS) NOAA-20 and NOAA/NASA Suomi-NPP, carry instruments not available on GOES, including a microwave sounding instrument, which allows scientists to see through clouds to what lies beneath. The polar satellites also carry the Day-Night Band, which enables scientists and forecasters to see cloud patterns at night, thanks to reflected moonlight.
How Many Satellites Orbit Earth
Each of the geostationary and polar-orbiting satellites carries an advanced imager for providing detailed images of Earth. The imagers have many “channels,” each designed to detect specific features, such as cloud type, atmospheric water vapor, ozone, carbon dioxide, or areas of ice or snow. Combining data from multiple channels provides even more information for forecasters.
NOAA also operates additional satellites in low-Earth orbit and a deep space satellite at Lagrange point 1, approximately one million miles away from Earth. On board NOAA’s DSCOVR satellite is NASA’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) instrument that watches Earth.
Earth Orbits The Sun

Different vantage points, geographic coverage, instrumentation, and imaging frequency from NOAA satellites offer unique information about our home planet. Together, they provide complementary measurements for a complete picture of what’s happening on Earth.
NOAA satellites see it all—hurricanes, severe thunderstorms, lightning, fires, dust storms, air quality, fog, volcanic eruptions, vegetation, snow and ice cover, flooding, sea and land surface temperature, ocean health and more. They can even track ship traffic and power outages. Every day, NOAA satellites provide critical information to keep us informed and help us stay safe. At NOAA, each day is Earth Day.
